Table 1 Characteristics of models. Tabulated characteristics are the simulation environment and integration method, phases of long-term potentiation and long-term depression, model inputs, model outputs chosen for this study, and size of the model based on the number of different chemical species or other model variables. Used abbreviations are α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid receptor (AMPAR), calcium ion (Ca2+), Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII), cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), dopamine (DA), DA- and cAMP-regulated neuronal phosphoprotein of 32 kDa (DARPP32), early phase LTP (E-LTP), induction (Ind.), Ca2+ influx via NMDARs (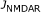 ), late phase LTP (L-LTP), long-term depression (LTD), long-term potentiation (LTP), N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR), and cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA).
), late phase LTP (L-LTP), long-term depression (LTD), long-term potentiation (LTP), N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR), and cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA).
Model | Simulation environment | Phases | Inputs | Outputs | Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
d'Alcantara et al. [16] | MATLAB, ode23 (explicit Runge-Kutta) | Ind. LTP/LTD | Ca2+ | AMPAR | 14 |
Kim et al. [17] | XPPAUT, adaptive stiff integration method | Ind. L-LTP | Ca2+, DA | CaMKII/PKA | 49 |
Lindskog et al. [18] | XPPAUT, adaptive stiff integration method | Ind. E-LTP | Ca2+, DA | DARPP32 | 89 |
Nakano et al. [19] | GENESIS/Kinetikit, exponential Euler | Ind. LTP/LTD | Ca2+, DA | AMPAR | 111 |
Hayer and Bhalla [2] | MATLAB, ode23s (based on Rosenbrock) | LTP/LTD | Ca2+, cAMP, | AMPAR | 258 |
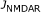 ), late phase LTP (L-LTP), long-term depression (LTD), long-term potentiation (LTP), N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR), and cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA).
), late phase LTP (L-LTP), long-term depression (LTD), long-term potentiation (LTP), N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR), and cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA).